Introduction: The Role of Valves in Fluid Control Systems
In modern industrial processes and infrastructure, valves are indispensable core components of any fluid control system. They act as the "heart" of the piping network, accurately regulating the direction, pressure, and flow rate of various media, such as water, oil, gas, and steam. The correct selection and utilization of valves are directly linked to the operational efficiency, safety, and economy of the entire system.
Among the many valve types, the Gate Valve, Globe Valve, and Check Valve are the three most common and widely applied in industrial settings. These three Gate/Globe/Check Valves differ significantly in their structural design, working principles, and functional applications, making each suitable for distinct operating conditions.
1. An In-Depth Look at Gate Valves
Working Principle of Gate Valves
The Gate Valve is a type of positive displacement or on-off valve. Its core operating principle involves a wedge-shaped gate (or disc) moving linearly, perpendicular to the flow path, to achieve the opening or closing action. When the stem lifts the gate completely, the valve passage is fully open, allowing fluid to pass through with minimal obstruction. When the gate is fully lowered, it provides a tight shutoff of the fluid.
This design makes the Gate Valve highly suited for simple on/off control. Structurally, the flow path is straight-through, which maximizes flow and minimizes fluid resistance inside the valve.
Typical Applications of Gate Valves
Due to their minimal pressure drop when fully open, Gate Valves are primarily used in applications that require infrequent operation and the valve must be either fully open or fully closed.
- On/Off Control: Used to isolate or connect media in pipeline systems.
- Large Diameter Applications: Widely utilized in water supply systems, oil and gas transmission pipelines, and other scenarios requiring large flow rates and low resistance.
For special and demanding service conditions, such as media involving high temperature, high pressure, strong corrosion, or ultra-low temperature, specialized alloy valves are crucial.
Trust Valve (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd., specializing in manufacturing special alloy valves in China since our Founding in 1997 and located in Funing Economic Development Zone, Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province, ensures that our Gate Valves are robust enough for reliable control in these extreme environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gate Valves
| Feature |
Gate Valves |
| Advantages |
Lowest pressure drop when fully open; relatively simple design; bi-directional flow capability; suitable for large bore pipes. |
| Disadvantages |
Not suitable for throttling; frequent operation or partial opening can lead to severe erosion of the seating surfaces; slow to open and close. |
The main drawback of the Gate Valve is its unsuitability for flow regulation, or throttling. Keeping a Gate Valve partially open for extended periods causes the high-velocity flow to severely wash and wear the seating surfaces, compromising its ability to seal tightly when eventually closed.
2. An In-Depth Look at Globe Valves
Working Principle of Globe Valves
Unlike the straight-through flow path of the Gate Valve, the Globe Valve is characterized by a bent or "S"-shaped internal flow channel. The valve operates by moving a disc (or plug) linearly toward or away from a seating surface, which is parallel to the direction of the flow. The fluid is forced to change direction within the valve body to pass through the port created by the disc and the seat.
This internal structure, which forces the fluid to change direction, is precisely what gives the Globe Valve its superior flow control capabilities.
Typical Applications of Globe Valves
The Globe Valve is the recognized choice for regulating (throttling) service. It can accurately modulate the flow rate of the medium to achieve precise process conditions.
- Flow Regulation and Throttling: Extensively used in systems requiring accurate flow control, such as cooling water systems and precise chemical dosing.
- Tight Shutoff: Due to the perpendicular closure mechanism, the Globe Valve achieves a tighter and more reliable shutoff compared to the Gate Valve, making it ideal for steam lines and applications requiring positive isolation.
Trust Valve (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd., main products include gate valves, globe valves, check valves, ball valves, gauge valves, gauge valve clusters, pigging valves, and other customized valves. These Globe Valves are designed and manufactured with stringent consideration for the demanding requirements of high temperature and high pressure service. We operate under rigorous quality systems, including ISO9001 Quality Management System certification, to ensure the reliable performance of every unit.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Globe Valves
| Feature |
Globe Valves |
| Advantages |
Excellent throttling capability; positive and tight shutoff; less seating surface wear during throttling. |
| Disadvantages |
Higher pressure drop compared to Gate Valves due to tortuous flow path; more complex design; typically restricted to unidirectional flow. |
The main disadvantage of the Globe Valve is that its pressure drop in the fully open position is significantly higher than that of the Gate Valve, leading to energy loss in applications where throttling is not required.
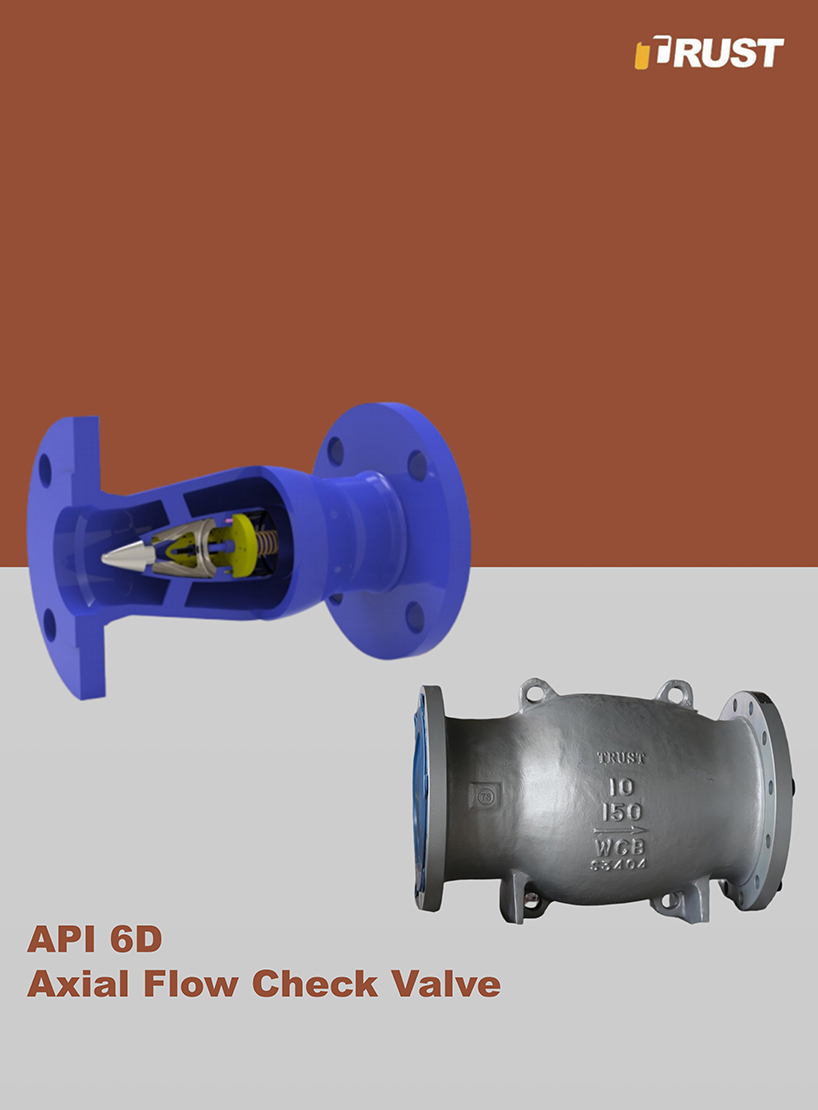
3. An In-Depth Look at Check Valves
Working Principle of Check Valves
The Check Valve, also known as a non-return valve, is a unique type of valve whose sole function is to prevent backflow prevention of the fluid. Unlike Gate Valves and Globe Valves which require an external actuator (like a handwheel or motor), the Check Valve is automatically operated. It relies entirely on the fluid's own pressure differential for opening and closing:
- During normal flow, the fluid pressure pushes the internal mechanism (disc, ball, or swing arm) open.
- When the flow stops or reverses (backflow occurs), the mechanism automatically closes under the force of gravity or reverse pressure, tightly preventing the fluid from flowing backward.
Main Types of Check Valves
Check Valves come in various designs to suit different pipe sizes, media types, and operating conditions:
- Swing Check Valves: The disc swings on a hinge, suitable for large diameters and low velocity.
- Lift Check Valves: The disc moves vertically within a guide, ideal for small diameters and high pressure.
- Ball Check Valves: The mechanism is a ball that seats when flow reverses.
Typical Applications of Check Valves
The Check Valve is vital for pipeline system safety, with applications focused on preventing reverse flow:
- Backflow Prevention: Installed at the discharge of pumps to prevent liquid from draining back and damaging the pump impeller upon shutdown.
- System Protection: Used in boiler feed water systems and any line where preventing contamination due to counterflow is critical.
In the manufacturing of Gate/Globe/Check Valves, Trust Valve (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. is equipped with over 100 sets of special lathes and CNC machining centers and maintains a complete set of inspection facilities. This allows us to perform required tests such as NDT (RT, UT, MT, PT), cryogenic testing, and fire-safe testing, ensuring that our Check Valves provide reliable backflow prevention even in the most severe service, such as ultra-low temperature. We manage our operations using an ERP system, supporting an annual production capacity of approximately 25,000 sets.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Check Valves
| Feature |
Check Valves |
| Advantages |
Automatic operation, requiring no external power or manual intervention; simple structure; effectively prevents backflow and protects upstream equipment. |
| Disadvantages |
Cannot be used for precise fluid control or throttling; rapid closure can cause sudden pressure surges known as water hammer. |
4. Key Differences Comparing Gate/Globe/Check Valves
Understanding the fundamental differences between Gate Valves, Globe Valves, and Check Valves is paramount for effective valve selection. These differences primarily lie in their method of flow control, resulting pressure drop, and design architecture.
| Feature |
Gate Valves |
Globe Valves |
Check Valves |
| Flow Control Function |
On/Off Only |
Throttling and flow regulation |
Unidirectional flow (backflow prevention) |
| Pressure Drop |
Lowest (when fully open) |
Highest (due to tortuous path) |
Low to medium (dependent on type) |
| Flow Direction |
Bi-directional (No restriction) |
Unidirectional (Generally restricted) |
Strictly unidirectional (Automatic closure) |
| Operation Type |
Manual/Automated (External power) |
Manual/Automated (External power) |
Automatic (Relies on fluid pressure differential) |
| Flow Resistance |
Low |
High |
Medium |
| Sealing Method |
Gate parallel to seat contact |
Disc perpendicular to seat contact |
Disc/Ball/Swing arm automatic seating |
Summary of Differences and Company Expertise
The table illustrates that the Gate Valve is an excellent isolation tool, valued for minimizing pressure drop; the Globe Valve is a precise modulating tool, valued for its superior throttling capability; and the Check Valve is a safety tool, valued for reliable backflow prevention.
The commitment to quality of Trust Valve (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. is affirmed by certifications such as HSE Environmental Health & Safety Management System, EU CE, API 607 Fire-Proof, and SIL. This ensures that all our manufactured Gate/Globe/Check Valves are built to a high standard, ready to perform reliably in demanding service conditions like those requiring high pressure and strong corrosion resistance.
5. Valve Selection Guide: How to Choose the Right Valve
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Valve
Selecting the correct valve is crucial for the efficient and safe operation of the piping system. When choosing among Gate/Globe/Check Valves, one must weigh the application requirements against the valve's characteristics.
- Fluid Type: Is the medium liquid, gas, or slurry? Is it corrosive or toxic? This dictates the required material, which is why our expertise in special alloy valves is so valuable.
- Pressure and Temperature Requirements: Conditions like high pressure, high temperature, or ultra-low temperature demand specific design standards and material compliance.
- Flow Control Needs: Is only full open/close required, or is precise throttling and flow regulation necessary?
- Operation Frequency: Will the valve be operated frequently or infrequently? (Frequent operation will hasten wear in Gate Valves).
- Special Certifications: Requirements for standards like API 600 (Gate Valve standard), API 607 Fire-Proof, or SIL functional safety.
When to Use Each Type of Valve
- Gate Valves: Use when the goal is to minimize pipeline resistance, achieve quick full isolation, and throttling is not required.
- Globe Valves: Use when frequent operation is required and precise flow regulation (throttling) is necessary, even at the cost of a higher pressure drop.
- Check Valves: Use when backflow prevention is a critical safety requirement, such as downstream of pumps or to prevent reverse contamination.
FAQ
What is the significance of the API 600 standard in relation to Gate Valves?
API 600 is the specification standard issued by the American Petroleum Institute (API) for flanged, bolted bonnet steel Gate Valves. It outlines the design, material, manufacturing, and testing requirements for these Gate Valves, serving as a critical foundation for high-quality gate valves used in the petroleum and natural gas industries.
Why does the Globe Valve cause a higher pressure drop than the Gate Valve?
The primary reason is the flow passage geometry. Gate Valves have a straight-through bore, allowing media to pass with minimal obstruction. In contrast, the internal flow path of the Globe Valve is tortuous (S-shaped or angled), forcing the fluid to change direction multiple times. This flow path creates significant localized resistance, resulting in a substantially higher pressure drop.
What is water hammer, and how does it relate to Check Valves?
Water hammer is a pressure surge or wave caused when a fluid in motion is forced to stop or change direction suddenly (e.g., when a pump stops or a Check Valve closes rapidly). Certain types of Check Valves, particularly those used in high-velocity services, can induce water hammer upon quick closure. To mitigate this, specialized slow-closing or cushioned Check Valves are often employed.
Can a Gate Valve be used for throttling?
While a Gate Valve can be partially opened for throttling in theory, it is strongly discouraged. As previously detailed, operating a Gate Valve in a partially open position causes the high-velocity fluid flow to impinge severely on the gate and seat surfaces. This accelerates erosion and wear, ultimately destroying the valve's ability to provide a tight shutoff for its intended on/off function.
 English
English русский
русский Français
Français 中文简体
中文简体 Português
Português Español
Español italiano
italiano عربى
عربى فارسی
فارسی

cryogenicvalves.jpg)





















 No.100 Xiejin Avenue, Funing County Economic Development Zone, Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province
No.100 Xiejin Avenue, Funing County Economic Development Zone, Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province  +86-515-87398111
+86-515-87398111  office@trustvalve.com
office@trustvalve.com 